2023 has been a turbulent year for the global economy, with Q2 marked by a series of risk events that have significant implications for future interest rate trends. These occurrences have caused rapid shifts between optimism and uncertainty, resulting in substantial market volatility. As we progress through the remaining months of the year, the global economy is anticipated to encounter further dynamic challenges. However, with each challenge comes the opportunity to thrive in turbulent times.
Despite a global downtrend in inflation, it remains a top concern for central bankers worldwide particularly in countries experiencing stubborn and persistent core inflation. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), year-on-year (YoY) inflation in G7 nations fell to 4.6% in May 2023, the lowest since September 2021, with a decline in all countries except the UK. The U.S. Federal Reserve (US Fed) responded to the decline by pausing its interest rate hikes in June 2023 after 15 consecutive months of increases. However, the pause is likely to be brief as the Fed has signalled its intention to resume tightening soon if inflation remains sticky. Moreover, most regions are showing signs of slowing growth, adding to the challenges faced by central bankers as they balance the need to contain inflation while supporting economic growth. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) warns that the global economic growth outlook for the next five years is the weakest in more than 30 years, highlighting the need for coordinated policy actions to mitigate risks and ensure sustained growth.
The US debt ceiling crisis was another major risk event that has significantly impacted financial markets. Once the $31.4 trillion debt ceiling was reached, negotiations between the White House and congressional Republicans hit a deadlock, causing market sentiment to plummet. This raised concerns of an unprecedented economic catastrophe, which could lead to market selloffs and a spike in borrowing costs. Fortunately, in the final week of May, an agreement was reached to raise the debt ceiling for two years as well as to cap spending. This allowed the debt limit to be suspended until January 1, 2025, enabling the Treasury to normalise its cash level, and bringing much-needed relief to financial markets.
Over in China, the pace of economic recovery has been sluggish, with recent data continuing to disappoint. For the third consecutive month, Chinese manufacturing activity remained in contraction mode, as June's Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) came in at 49 points. This can be attributed to weak domestic consumption and global demand, which have been a drag on the nation's growth. To support the recovery, the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) made its first cut in 10 months by lowering its 7-day reverse repo rate by 10 bps to 1.90% in June 2023.
In Malaysia, gross domestic product (GDP) grew by a robust +5.6% YoY in Q1 2023, driven by a strong recovery in the services sector, tight labour market, and resilient trade sector. However, growth in the coming quarters may weaken due to cooling external demand, fading reopening tailwinds, and weaker business sentiment amid elevated global uncertainty. Despite these challenges, Malaysia's growth is supported by healthy domestic demand, a recovering tourism industry, and a strong labour market, which has led Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) to maintain its GDP growth forecast of 4% - 5%. At the same time, headline inflation fell below 3% YoY in May 2023, the first time in a year. The projected inflation range for 2023 remains unchanged at an average of 2.8% - 3.8%. In May 2023, BNM raised the Overnight Policy Rate (OPR) by 25 basis points (bps) to 3.00%, with future decisions to be data dependent.
Equity market
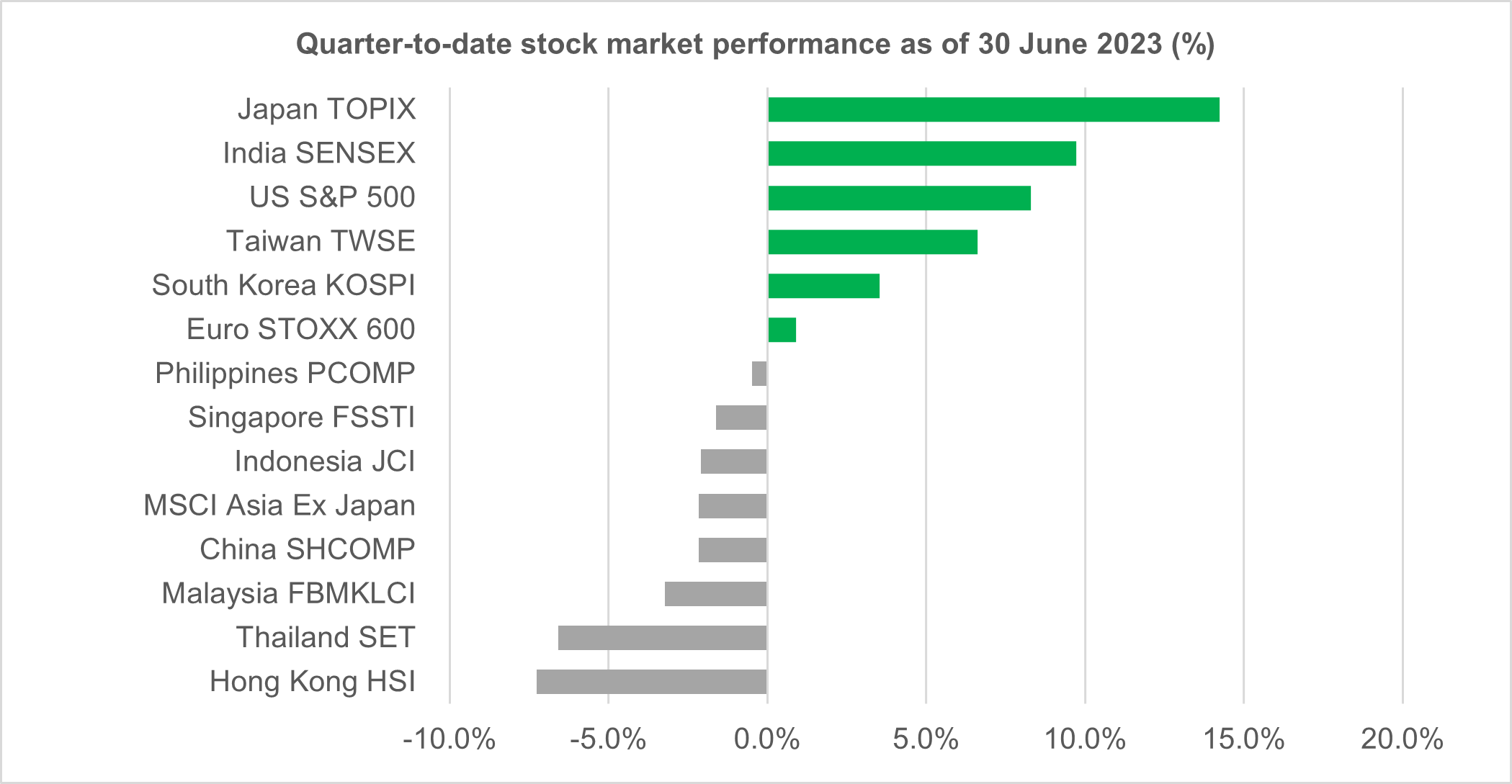
In Q2 2023, the global stock market experienced a mix of gains and losses. April kicked off on a strong note, with positive economic data indicating a resilient global economy. Surpassing expectations, inflation data, manufacturing figures, and China's 1Q GDP results fuelled optimism across markets, resulting in robust gains for most stock indexes. However, the tides turned in May as concerns grew over a potential US debt default. This led to a decline in market performance, erasing a significant portion of the earlier gains. But in late May, NVIDIA's strong earnings guidance triggered an AI boom, sparking substantial gains in technology-heavy indices. This rally extended into June, with technology-heavy indices like the US S&P500, Taiwan's TWSE, and South Korea's KOSPI finishing the quarter positively. Meanwhile, Japan's TOPIX emerged as the top performer, reaching a three-decade high. Factors such as impressive earnings growth, share buybacks, attractive valuations, and a weakened Yen enticed foreign investors.
While most developed market indexes performed positively in Q2 2023, the same could not be said for most regional Asian indexes. Market sentiment was dampened by concerns over the US debt default and China's weakening growth, leading to a more lacklustre performance. Hong Kong's HSI and Thailand's SET finished at the bottom of the barrel for the quarter, with returns of -7.3% and -6.6%, respectively. Overall, the MSCI Asia ex Japan Index suffered as a whole, returning a modest -2.2% quarter-on-quarter (QoQ).
Looking at the local Malaysian equity market, the FBMKLCI experienced a challenging Q2. Corporate earnings reported for the first quarter were generally weak, attributed to lower external demand, normalising domestic spending, and higher input costs. Adding to the woes, the local bourse also suffered outflows from foreign funds, in line with regional peers. Foreign investors have been sellers for 20 out of 26 weeks in year-to-date June 2023, with a net foreign outflow of -RM4.19b1. As a result, the FBMKLCI underperformed, with a weak performance of -3.2% QoQ.
With ongoing risk events such as the US debt crisis and inflation, uncertainties in the market became worse, prompting investors to seek refuge in defensive sectors. As a result, the Utilities sector emerged as the best performing sector in the quarter.
In the broader market, the FBM100 Index and the FBM Small Cap Index both returned -2.7%, mirroring the FBMKLCI's downward trend.
As we move into 2H23, global equity markets are expected to continue experiencing high volatility due to various factors such as a possible mild recession in the US, elevated global inflation, and geopolitical tensions. Despite these uncertainties, there are early signs of the economy bottoming out, and we remain cautiously optimistic about the equity market's performance in 2H23. To navigate this challenging period, we believe in maintaining a well-balanced portfolio with a focus on attractively valued dividend-yielding stocks and firm fundamentals.
Source: Bloomberg, as of 30 June 2023. Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
Fixed income market
Q2 2023 was a volatile quarter for the US Treasury (UST) yields, with significant fluctuations observed throughout the period. Overall, the 2-year, 5-year and 10-year UST yields changed +87bps, +58bps and +37bps, to close at 4.90%, 4.16% and 3.84% respectively. While April saw only a marginal decline, yields started rising in mid-May and continued to increase throughout June. This was due to concerns over a potential US debt default, which intensified as negotiations failed to make progress.
Despite the US Fed's decision to pause hiking interest rates in June, comments from US Fed Chair Jerome Powell painted a more hawkish view, indicating that the Fed is not done battling inflation yet and any future rate hikes would be data dependent. Furthermore, the release of strong economic data in June, including a notable decline in initial jobless claims and a significant upward revision in the US' 1Q GDP, has demonstrated the resilience of the US economy. While this has eased concerns about a potential recession, it has also raised the possibility of the Fed extending its restrictive monetary policy for a longer period than expected.
For the local market, the Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) yield curve bull flattened. The 3-year and 5-year MGS saw increases of 13bps and 7bps respectively, while the 10-year MGS yields decreased by 6bps. As a result, the quarter ended with the 3-year, 5-year, and 10-year MGS yields closing at 3.48%, 3.61%, and 3.84% respectively.
We remain positive on the medium-term outlook for the Malaysian bond market as we anticipate the end of BNM's rate hike cycle. While economic growth is subdued and inflation levels are manageable, we exercise caution to potential OPR hikes in the future if inflation surprises or if the UST sells off. In the short-term, we expect a high level of market volatility globally as investors keep a close watch on central bank actions. Key considerations include where terminal interest rates will peak and the duration for which interest rates will be maintained at elevated levels. Additionally, extraordinary events such as the prolonged Russia-Ukraine conflict and ongoing US-China tensions have contributed to increased uncertainties in the region. Given these factors, we remain vigilant and will closely monitor global developments to gauge market reactions.
Download full PDF View key takeaways
Source:
1MIDF Research, as of 30 June 2023